Each month the California Employment Development Department (EDD) releases employment data for the prior month. This edition of San Diego’s Economic Pulse covers July 2020 and reflects some effects of the coronavirus pandemic on the labor market. Check out EDC’s research bureau for more data and stats about San Diego’s economy.
Unemployment Slightly Lower
The region’s unemployment rate was 12.3 percent in July down from a revised 13.8 percent in June 2020, and far above the year-ago estimate of 3.6 percent. Unemployment declined monthly as the region continues to reopen and jobs recover. The region’s unemployment rate remains lower than the state unemployment rate of 13.7 percent, but higher than the national unemployment rate of 10.5 percent.
Unemployment was highest in the unincorporated areas of Bostonia (21.8%), Bonita (18.0%), Spring Valley (16.7%), and in the cities of National City (16.5%) and El Cajon (16.4%). Unemployment was lowest in the cities of Solana Beach (6.9%), Poway (8.6%), Coronado (9.1%), and Del Mar (9.1%). Areas with large Hispanic populations are facing higher rates of unemployment, as Hispanics are disproportionally employed in the most vulnerable occupations.
Employment Continues to Decline
Total nonfarm employment fell in July, down 2,200 jobs. This differs from state and national data. In California, nonfarm employment increased by 15,370 in July from the month prior, while payroll employment increased by 1.8 million in the U.S. during the same time period.
Compared to a year ago, San Diego nonfarm employment remains down 144,400 jobs, or 10.2 percent. In California, total nonfarm employment is down 1.6 million jobs, or 8 percent compared to a year ago, while the U.S. is down nearly 13 million jobs, or 8.8 percent.
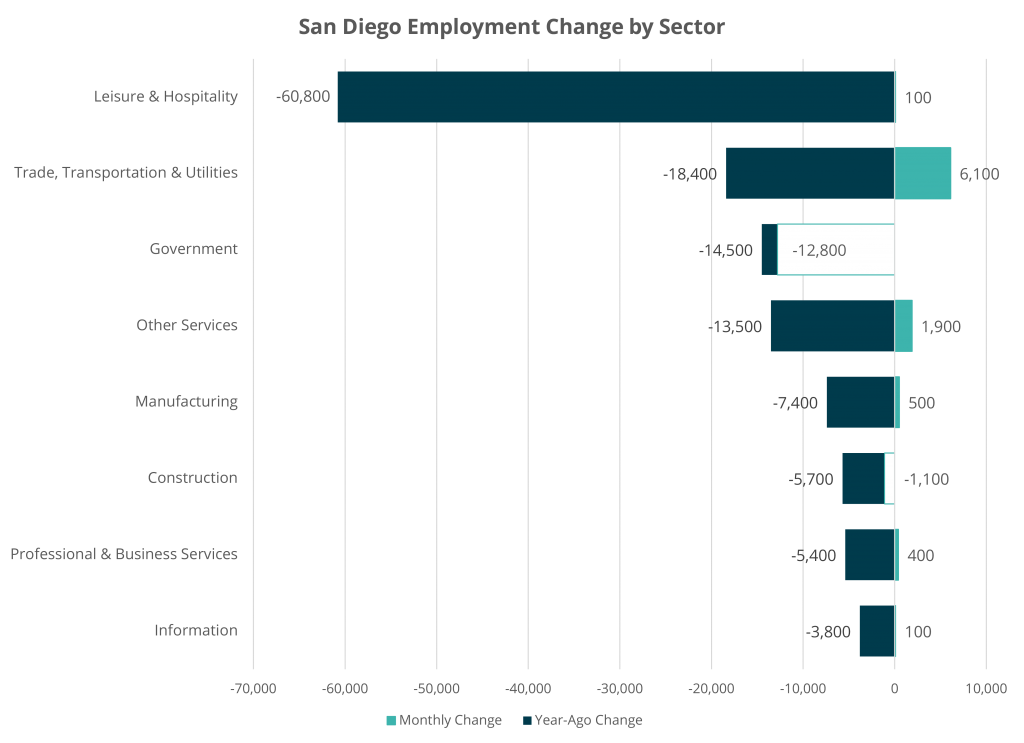
Sector Employment Split on Gains
Government accounted for the largest monthly losses, losing 12,800 jobs in July, primarily concentrated in local government education (down 13,200 jobs) and state government education (down 500 jobs). Compared to a year ago, local government education is down 8,300 jobs, and state government education is down 4,900 jobs. Local government education employment is largely women occupied (70 percent). Job losses in local and state government education have the potential to set back women in the workforce, a trend already exasperated by the pandemic according to a United Nations report.
Construction followed with a decline of 1,100 jobs. Construction of buildings declined both monthly and annually, which is especially important as the region continues to grapple with a housing affordability crisis. Without construction jobs, home building stops. Home price growth continues to outpace incomes, as housing production is about half the rate necessary to keep up with job and population growth. Ensuring San Diego is an attractive and affordable place for talent and business is critical to maintaining its regional competitiveness.
Trade, transportation, and utilities employment increased this month, adding 6,100 jobs. This was driven primarily by retail, which added 4,200 jobs. Clothing and clothing accessories stores grew by nearly 13 percent in July. As California clarified social distance retail guidelines, many retail stores were able to reopen, leading to an increase in employment.
The leisure and hospitality industry gained back 100 jobs in July, but remains down 60,800 jobs compared to a year ago. Nearly 40 percent of leisure and hospitality industry employees are Hispanic. These jobs are not likely to return in large numbers while social distancing remains in effect.
A Long Road to Recovery
Industry employment remains well below pre-pandemic levels seen in February 2020. The largest decline in employment has been the leisure and hospitality industry, down 49,500 jobs, or 25 percent. Government employment is down 30,200 jobs, educational and health services is down 20,300 jobs, and trade, transportation, and utilities, which includes retail, has lost 18,000 jobs since February.
While some jobs have been recovered, many will be lost permanently. Creative training programs to get these workers employed in growing occupations will be key to our economic recovery. Furthermore, the pandemic has exacerbated the inequities that have long-plagued the region, particularly our Hispanic population. Developing an economic recovery strategy that promotes inclusive growth is essential to ensuring our future economic competitiveness.
For more COVID-19 recovery resources and information, please visit this page.
EDC is here to help. You can use the button below to request our assistance with finding information, applying to relief programs, and more.
You also might like: