On August 14, EDC hosted its second Inclusive Growth Roundtable of the year, convening 40 regional stakeholders, service providers, and small business leaders to share the latest data on quality small business jobs and ground-truth our findings.
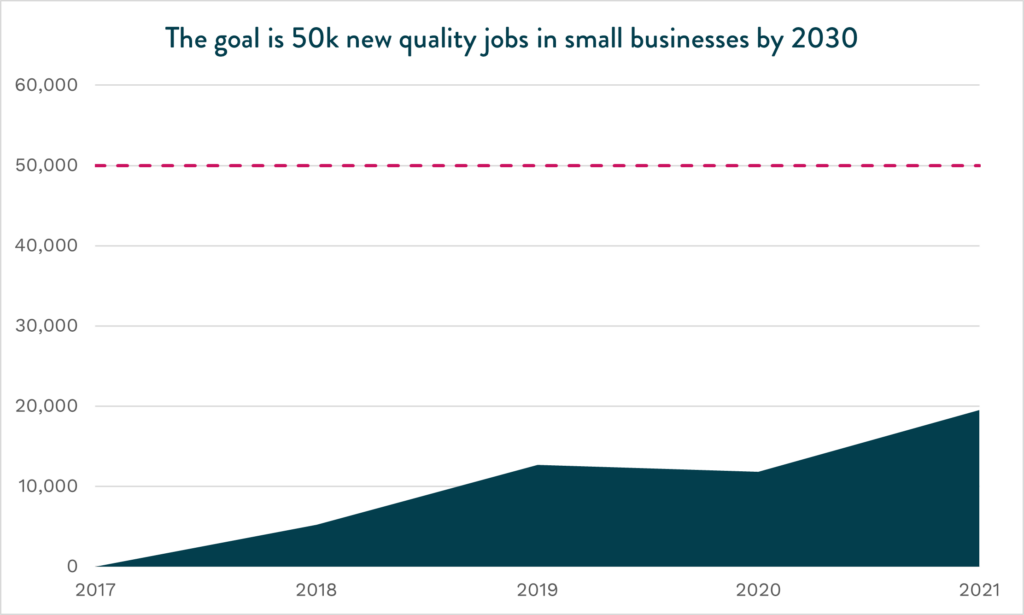
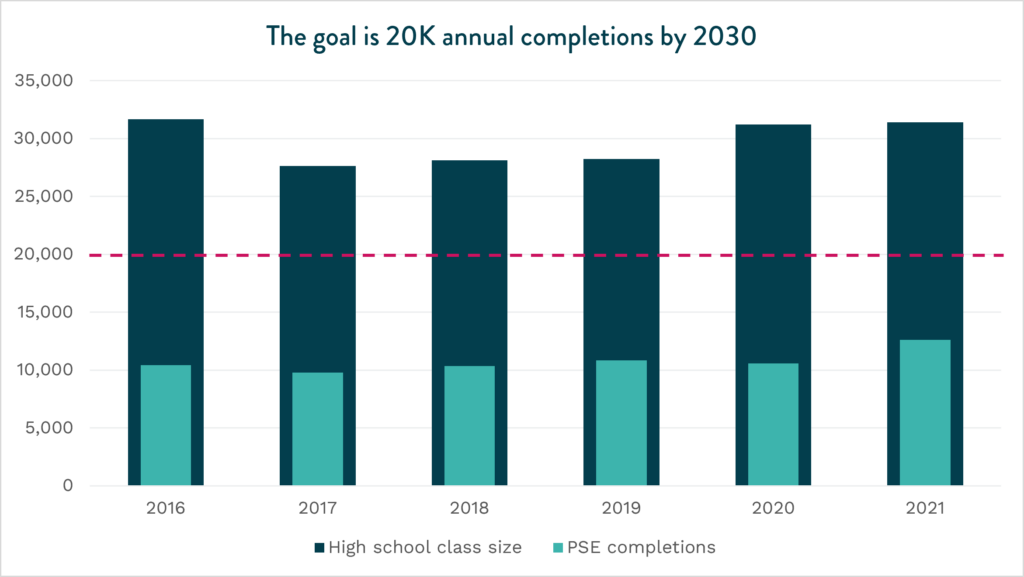
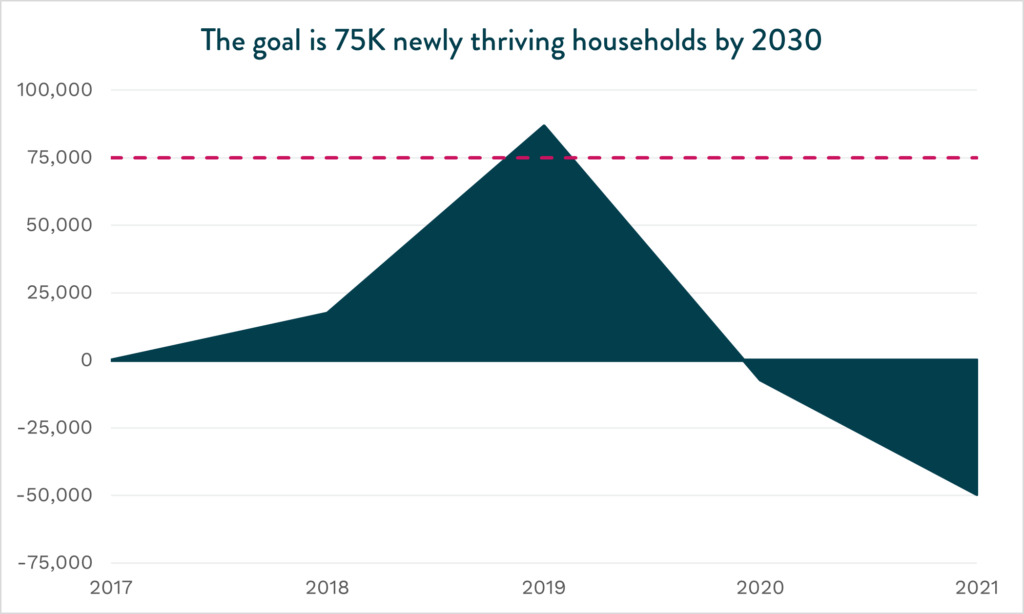
The 2030 Inclusive Growth goals focus on three key pillars core to any strong regional economy: quality small business jobs, a skilled talent pipeline, and thriving households. EDC analyzes the region’s progress to each goal annually. During the August gathering, we focused specifically on the region’s progress toward adding 50,000 new quality small businesses jobs by 2030. EDC currently defines a quality job as a business with fewer than 100 employees that offers at least $23 per hour and provides health insurance.

EDC’s Vice Chair of Inclusive Growth Lisette Islas kicked off the dialogue reminding us why this work matters, and celebrating the intentional and collaborative journey we have been on as a region since 2017. We’ve seen significant progress in San Diego becoming a more inclusive economy, but there is more work to be done. Below is a recap of the data shared, insights gathered, and issues we see on the horizon.
The backbone of San Diego’s economy
In San Diego, small businesses represent 98 percent of all firms and account for 59 percent of total employment. The impact that small business owners have on local jobs cannot be overstated. Despite significant contributions, small businesses struggle to keep up in an increasingly expensive market.
The smaller the business, the larger the challenge for providing a competitive wage. In fact, small businesses offer 38 percent lower average wages compared to companies with more than 100 employees. Microbusiness (<4 employees) face the largest challenge when it comes to relative compensation. This trend has worsened since EDC began tracking quality jobs data in 2017, with the relative wage gap widening even more last year.
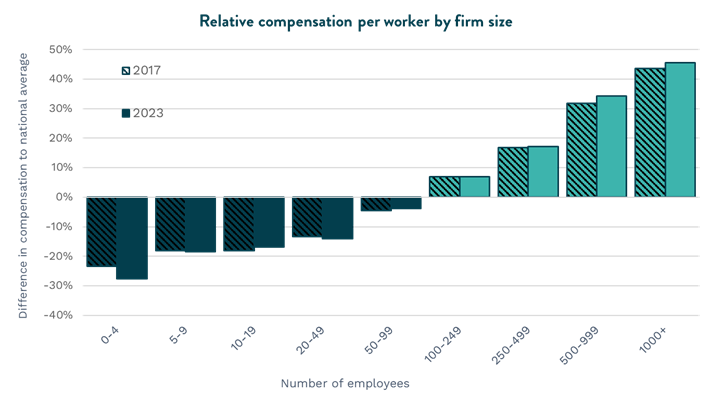
Quality small business jobs surge
The latest data shows that small businesses have steadily increased the proportion of quality jobs, with 28.8 percent of all small business jobs now meeting the wage threshold including health benefits. The latest data refresh shows that quality small business jobs surged last year. So much so, the region has nearly surpassed the 2030 Inclusive Growth goal, adding 48,481 new quality jobs.**

The data is gratifying and certainly reflects the importance and impact of efforts to increase opportunities for more small business owners, but there is more than this metric to unpack.
Inclusive Growth remains paramount
The world has changed dramatically in the last seven years since EDC launched the Inclusive Growth Initiative. In that time, the region experienced tremendous economic growth followed by a global pandemic that curtailed progress. Those hit the hardest were women and people of color in San Diego. Since then, we’ve seen a strong economic recovery, yet rising tides have not lifted all boats.
San Diego’s lowest paying occupations are disproportionately held by marginalized and under-invested-in populations. While the surge in quality jobs is reassuring, the reality is that more than two-thirds of small business jobs still fall below the wage threshold and larger businesses still have the advantage when it comes to paying competitive wages.
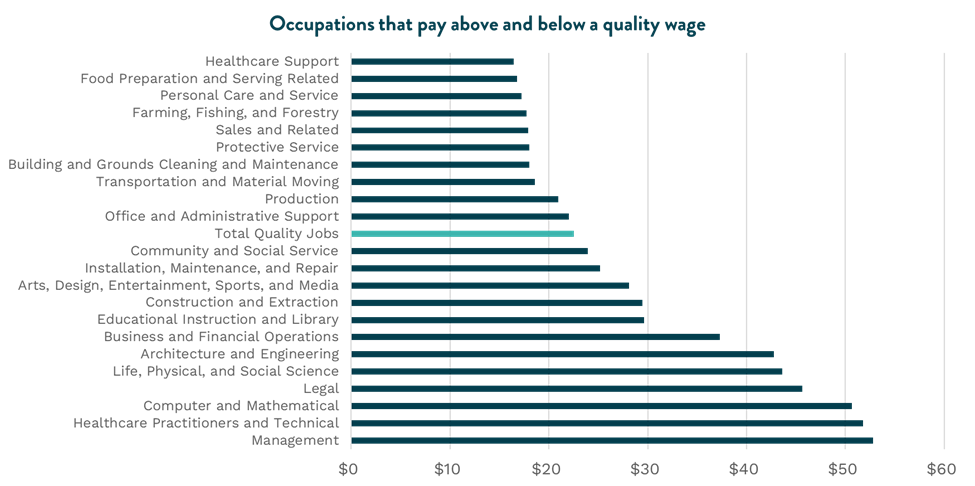
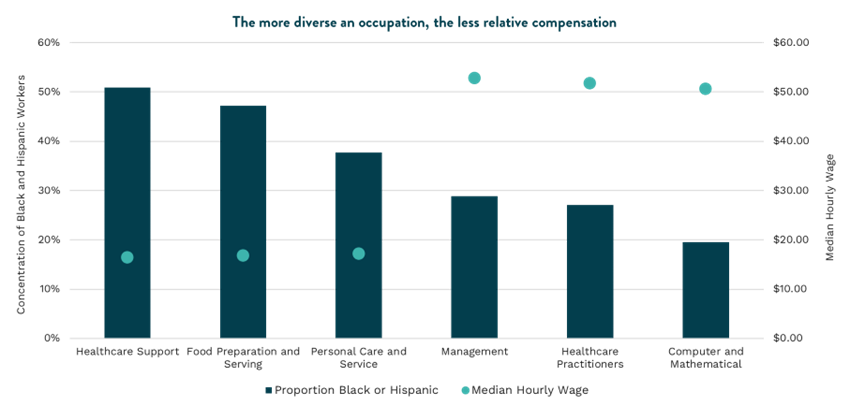
Also important to note, lower paying jobs are disproportionately held by people of color who are noticeably underrepresented in the highest paying occupations in town. For example, more than half of Healthcare Support occupations in San Diego, which include nursing, medical, and dental assistants, are held by Black or Latino people, but the average total wage is below $20 per hour. Conversely, less than 20 percent of Computer and Mathematics occupations, which include statisticians, programmers, and software developers, are held by Black and Latino people but pay more than $50 per hour on average.
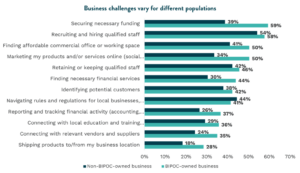
During the event, we also shared recently conducted survey results of 603 local small business owners which found that people of color have contrasting challenges when it comes to owning a business. Done together with SBDC, the survey results revealed that securing necessary funding is a major challenge for nearly two-thirds of minority small business owners. This highlights the importance of programs that tailor outreach, education, and funding resources for minority business owners to stay competitive in San Diego.
EDC’s commitment to increasing quality small business jobs with an inclusive lens is embedded into our programmatic work, yet we recognize that the road ahead will require sustained regional collaboration. We invite you and your organizations to join this movement so that San Diego remains competitive, and that all businesses and their employees continue to benefit from the region’s economic success.
- Endorse the Inclusive Growth goals
- Learn more about our programs and initiatives
- Join us for upcoming events and discussions

Bree Burris
Sr. Director, Communications & Community Engagement
** A previous version of this blog incorrectly stated 30.3 percent of all small business jobs now meet the wage threshold including health benefits, and that small businesses added 60,234 new quality jobs to the region, surpassing our Inclusive Growth goal. The data has been corrected and updated in line above as of September 5, 2024.


 One inspiring moment was when our group heard from Alesha Washington, CEO of the
One inspiring moment was when our group heard from Alesha Washington, CEO of the  For decades, the inclusion challenge was left only to the social services and philanthropic community to solve. Now, the business case has been made and it is clear inclusive growth is imperative to the region’s competitiveness. Without it, industry too will cease to thrive.
For decades, the inclusion challenge was left only to the social services and philanthropic community to solve. Now, the business case has been made and it is clear inclusive growth is imperative to the region’s competitiveness. Without it, industry too will cease to thrive.

 “EDC’s recent analysis underscores the significant impact of the pandemic on San Diego’s under-resourced communities and small businesses,” said Julian Parra, Business Banking Region Executive at Bank of America and EDC Board Chair. “To drive meaningful economic change, a diverse set of stakeholders must step up or the issues facing our economy—talent shortages, skills gaps, and a soaring cost of living—will further challenge San Diego’s economic competitiveness.”
“EDC’s recent analysis underscores the significant impact of the pandemic on San Diego’s under-resourced communities and small businesses,” said Julian Parra, Business Banking Region Executive at Bank of America and EDC Board Chair. “To drive meaningful economic change, a diverse set of stakeholders must step up or the issues facing our economy—talent shortages, skills gaps, and a soaring cost of living—will further challenge San Diego’s economic competitiveness.” “Employing more than 1,200 San Diegans, we understand the criticality of large employers fostering a robust talent pipeline who can afford to live and thrive here,” said
“Employing more than 1,200 San Diegans, we understand the criticality of large employers fostering a robust talent pipeline who can afford to live and thrive here,” said