Welcome to the fifth edition in EDC’s Changing Business Landscape Series, which will be published bi-monthly in the San Diego Business Journal and here on our blog. If you missed them, check out all past editions here.
Surveying the changing business landscape in San Diego
The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted every facet of life, including how businesses operate. Companies in every industry are rapidly re-evaluating how they do business, changing the way they interact with customers, manage supply chains and where their employees are physically located. This has massive immediate and long-term implications for San Diego’s workforce and job composition, as well as regional land use decisions and infrastructure investment.
To identify evolving trends in local business needs and operations, ensuring their ability to grow and thrive in the region, San Diego Regional EDC is surveying nearly 200 companies in the region’s key industries on a rolling basis throughout 2021 to monitor and report shifts in their priorities and strategies. In addition, EDC constructed the San Diego Business Recovery Index (BRI)—a sentiment index to measure companies’ perceptions of current conditions, as well as expectations for the future across several factors such as business development, employment, and commercial real estate needs. (An index value >50 reflects expansion, and a value <50 reflects contraction. More information on the index and how it is calculated is available here.)
These insights will help inform long-term economic development priorities around talent recruitment and retention, quality job creation, and infrastructure development. Companies are surveyed on several topics, with varying emphases in each wave.
Here are three key findings from the wave of surveying conducted in October 2021:
- For software companies, the struggle is now real. They have been among the most optimistic industries surveyed, but now face similar challenges to other industries.
- The market for skilled talent has never been hotter. A great convergence of talent needs is turning hiring difficulties into slower job growth.
- Supply chain disruptions appear to be pinching profit margins. Input prices have risen for many companies, but most are reluctant to pass along higher costs to their customers and opting to sacrifice earnings for now.
The BRI took a step back in October to settle at 54.1, marking the second consecutive decline since June. The topline index value edged 1.2 points lower from August’s 55.3 but is 9.6 points off its June high of 63.7. The deterioration stems from weaker perceptions of present conditions, but slightly more hopeful views of the future helped keep the overall BRI in expansion territory.
Companies reported a slowing of both revenues and earnings. This comes after a period of record earnings in some industries but could also be the result of prolonged supply chain disruptions that have choked off necessary inputs and simultaneously prevented sales. Yet, businesses surveyed also expressed continued difficulty hiring and retaining workers, driving a significant slowdown in job growth.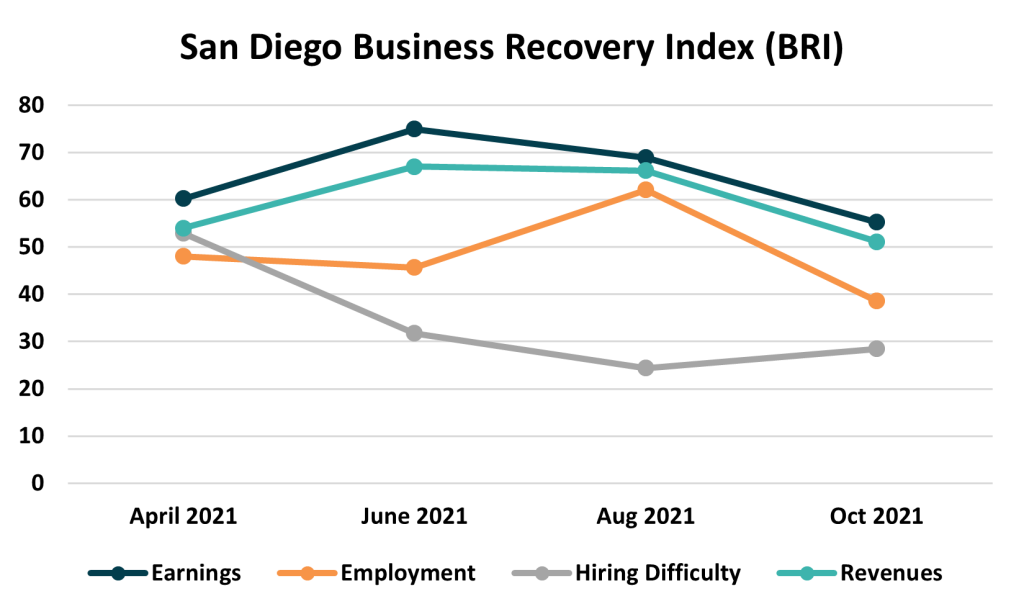
For tech companies, the struggle is now real
Firms in industries with limited remote work capabilities, such as Healthcare and Aerospace, continued to express relatively pessimistic views. Joining this list are Information and Communications Technology (ICT) and Software companies, which up to now have been among the most optimistic industries surveyed.
Software companies signaled revenues have begun to fall, along with an even steeper decline in earnings. Supply chain disruptions play a role here, as San Diego is top 10 exporter of services. Limited availability of or access to key inputs, as well as travel restrictions, have hindered San Diego Technology companies from growing their businesses. Making matters worse, these businesses also expressed far greater difficulty finding people to hire compared to the summer months, which is driving a significant slowdown in job growth. Taken together, these headwinds led respondents to sour on the economy—both presently as well as future expectations for the next six months to a year.
ICT firms have also lost some faith in their current and future economic prospects. Companies in this vertical are facing even greater supply chain difficulties than Software firms. Business development and hiring pose far greater challenges than they did in the summer. Worse still, worker retention has become nearly impossible as a record number and a record rate of people quit their jobs in September.
The market for skilled talent has never been hotter
Talent recruitment and retention challenges have undermined employers since before the pandemic began. What is new is employers reported a sharp slowdown in job growth as workers drive a hard bargain. Not only are workers seeking higher wages and more flexible work arrangements, but employers find themselves competing across industry for an increasingly limited pool of skilled talent.
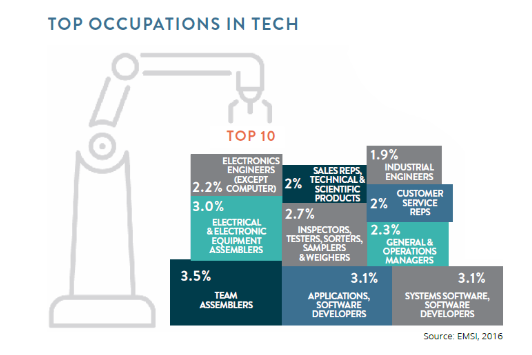
The top posted occupation in San Diego during the last year, outside of registered nurses, was for software developers and software quality assurance testers. There were more than 23,000 unique job postings for those occupations going back to October 2020. The top posting companies for these jobs are tech giants, such as Qualcomm and Apple, as well as startups receiving record venture funding. However, manufacturers comprised a formidable second with 4,514 unique positions during that time.
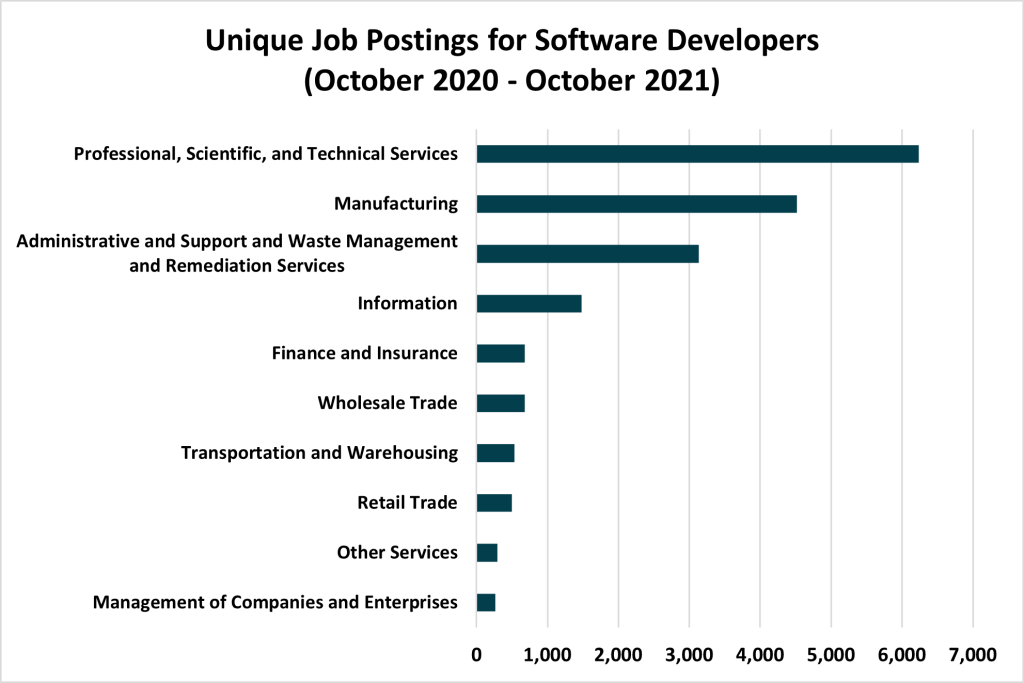
Manufacturing in San Diego has long been advanced—producing everything from jet engines to medical devices—so elevated demand for software developers working on unmanned aerial systems or DNA sequencing may not be all that surprising. Nevertheless, digging a bit deeper, we find the second most listed skill among Manufacturing job postings was for Teradata SQL, an open-source database management system. In fact, during the past 12 months, Manufacturing job postings that included Teradata SQL quadrupled and represent nearly 71 percent of all postings seeking that skillset. The median advertised annual salary for jobs requiring this skillset is $126,000, which is up 40 percent from a year earlier, and about $5,000 more than in either San Francisco or San Jose, and about $30,000 more than in Seattle.
The demand for skilled talent is rising rapidly and spreading across industries. Unfortunately, the supply of that talent has not kept pace. In fact, census data show an overall decline in the number of total degree holders in the region since 2017. A rising cost of living against a backdrop of increasing competition from “tech markets” across the globe poses a real challenge for local companies. With still more than 86,000 people unemployed, it has never been more important that the region invest in upskilling and building a pipeline of local talent to fuel San Diego’s recovery and future growth.
Supply chain disruptions appear to be squeezing profit margins
Supply chain disruptions and inflation continue to dominate headlines. While these challenges appear to be temporary, they are impacting consumers and the business decisions of local companies. Companies surveyed indicated supply chains are just as challenging now as they were in June. Furthermore, these challenges are directly tied to increases in input prices. This is leaking downstream into business development and sales, which employers, on balance, now rate as only slightly expansionary.
As such, some companies are considering passing along higher input costs as margins get squeezed from both sides. This decision largely depends on the magnitude of price increases that companies are facing themselves. Most companies are willing to absorb the bulk of increased costs when those increases are relatively small; tolerance for deeper margin cuts were much smaller. Only one in four companies indicated wanting to pass along at least half of those increased costs, where input prices have risen less than five percent. However, companies are nearly twice as likely (44 percent) to do so where input prices rose more than five percent—principally those in Manufacturing.
Passing along increased costs is a short-term strategy to a complex problem. As such, some companies are reevaluating their supply chains, not just in terms of suppliers but also the networks they rely upon to receive inputs or distribute products. Of the companies surveyed, only 14 percent indicated currently using the Port of San Diego. However, nearly double (27 percent) expressed a willingness to do so in the future.
The survey results continue to reflect an uneven recovery across industries. The reported trends in employment line up squarely with recent jobs reports for the region. In total, San Diego establishments added an underwhelming 3,600 jobs to the economy in September. The sharp slowdown in job growth helps explain the upward shift in remote work adoption as well as future expectations for remote work accommodations. There are many surveys of workers, both locally and nationally, indicating that desires for flexibility and remote work are strong and sticky. Despite these challenges, employers surveyed remain optimistic about the next six to 12 months albeit somewhat more modest plans for expansion.
Stay tuned for more on San Diego’s changing business landscape. EDC will be back every other month with more trends and insights. For more data and analysis, visit our research page.
This research is made possible by: